Discover how proper localization—beyond just translation—helps boost your website’s visibility, engagement, and sales in the Chinese market.
How Do Western Websites Different from Their Chinese Versions?
If you compare McDonald’s or Starbucks’ English websites with their Chinese counterparts, you’ll notice significant differences.
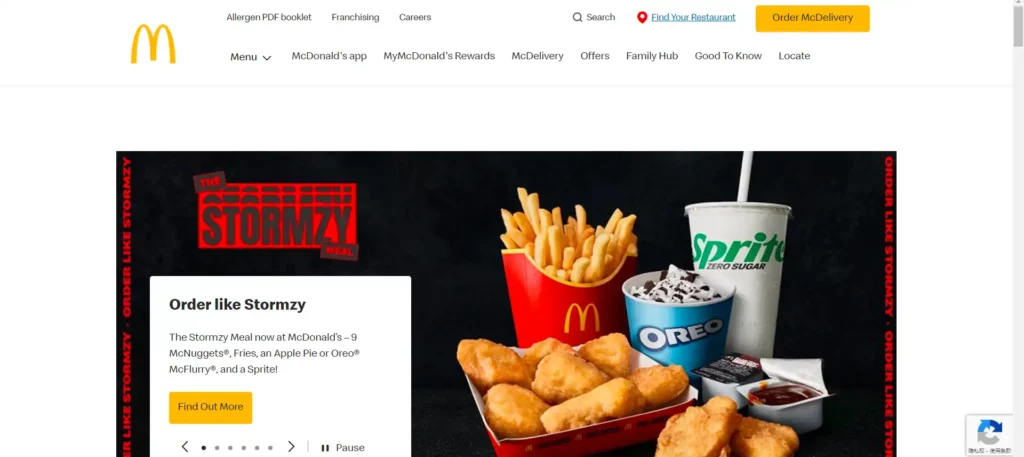
McDonald’s Engish
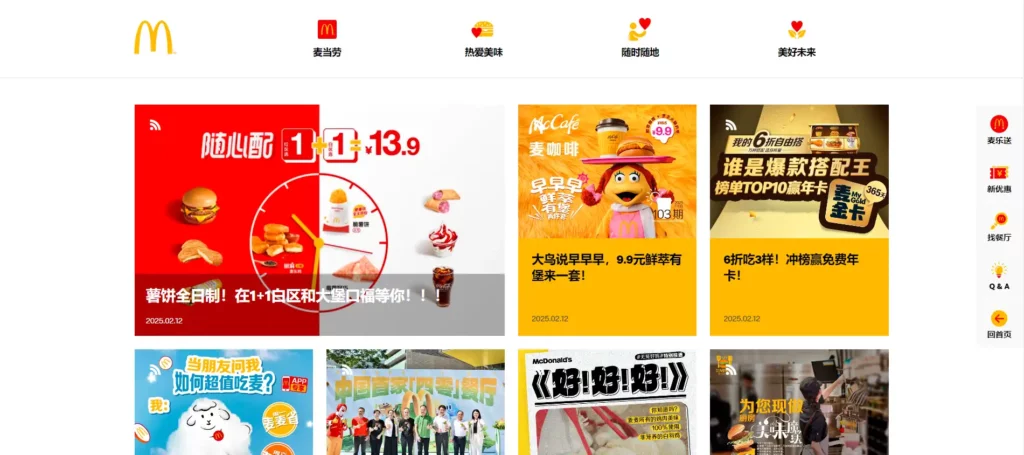
McDonald’s Chinese
Why?
Website localization involves more than just language. It adapts:
Colors & visuals – Different cultures associate colors with different emotions.
Website structure – Chinese users prefer dense, information-rich layouts.
Content tone & messaging – What works in the West might not resonate in China.
Call-to-action (CTA) placement – Chinese users expect quick access to promotions.
Key Takeaway: Some Western best practices don’t work in China—websites must be tailored to fit local browsing habits.
How Does Localization Impact E-Commerce Sales?

According to Deloitte’s report on China’s retail landscape, Chinese consumers:
Are tech-savvy and mobile-first.
Use social media (WeChat, Xiaohongshu) to influence buying decisions.
Expect seamless online shopping experiences in their native language.
💡 Real Case: Coach’s Weibo Campaign Skyrocketed Engagement
When luxury brand Coach launched its “Footprints” campaign on China’s Weibo, they didn’t just translate copy—they fully localized visuals, hashtags, and campaign timing around Chinese holidays. In just five days, they saw a 157% increase in followers and a 50% boost in engagement. This wasn’t luck—it was the result of understanding local platforms, mobile-first behavior, and cultural relevance. That’s the power of strategic localization.
📊 Research Insight:
A study on Website Localization in the Chinese Market (Singh, Fassott, Chao, Hoffman) found that effective localization increases purchase intent and creates favorable attitudes toward a website.
Key Takeaway: Consumers are more likely to buy when websites are culturally adapted—not just translated.
Do Localized Websites Have Higher Engagement?
Studies show that users spend more time on websites in their native language.
📊 Common Sense Advisory Survey (2,430 respondents, 8 countries):
72.1% prefer browsing websites in their native language.
72.4% are more likely to buy products when product info is in their language.
Key Takeaway: Localization isn’t just about translation—it’s about enhancing user experience and building trust.
Why Does China Block So Many Websites?
China has strict internet regulations that control access to foreign websites. The government blocks many Western platforms, including Google, Facebook, YouTube, Twitter, and Instagram, for several reasons:
Censorship: The government wants to control political and social narratives.
Economic Protectionism: Encourages the growth of domestic platforms like WeChat, Baidu, and Alibaba.
Data Control: Prevents foreign companies from collecting data on Chinese users.
Key Takeaway: Businesses that want to operate in China must adapt to local regulations and use Chinese digital platforms.
What is the Great Firewall of China?
The Great Firewall of China refers to the government’s internet censorship system, which filters, blocks, and controls online content.

Blocks foreign websites – Google, Facebook, WhatsApp, Twitter, etc.
Filters keywords and content – Sensitive topics are automatically flagged.
Requires companies to comply with regulations – Businesses must host websites on Chinese servers and use approved platforms.
Key Takeaway: If you want your website to work in China, you must follow local rules and optimize for Baidu instead of Google.
Why is Google So Slow in China?
Google services are either completely blocked or extremely slow in China because of the Great Firewall.
Why does this happen?
Government Restrictions: China blocks most Google services, including Search, Maps, and Drive.
Slow VPN Access: Many businesses and users rely on VPNs to access Google, but they’re often unreliable.
Preference for Local Alternatives: Chinese users primarily use Baidu, WeChat, and local platforms for search and services.
Key Takeaway: If your website depends on Google services (Analytics, Fonts, Captcha), it may not work properly in China. You must replace Google tools with China-friendly alternatives.
What Are the Key Takeaways for Chinese Localization Strategies?
Localization is both an opportunity and a challenge—especially in a competitive market like China.
Industry Insight:
Esmond K.L. Quek, former CEO of Hill & Knowlton China, shared an important lesson in an interview with China Daily:
“Multinationals that entered the market early are evolving and responding to customer demands much quicker than before. But new companies coming to China must learn from past lessons to avoid unnecessary mistakes.”
What Should Companies Focus On?
Product adaptation – Modify products to fit Chinese consumer needs.
Pricing strategy – Align with local economic conditions.
Promotion & branding – Use localized marketing strategies (social media, influencers, live streaming).
Distribution & logistics – Optimize supply chains and payment systems (Alipay, WeChat Pay).
Key Takeaway: Digital assets like websites, e-commerce platforms, and online marketing campaigns must be localized to maximize impact.
How Can You Get Started with Localization?
🚀 Start right this year with a localization strategy that works!
📩 Check out AZ-Loc’s Localization Page to learn how we can help you:
✅ Create high-quality localized content.
✅ Optimize your website for Chinese users.
✅ Increase engagement and conversions.
READ MORE>>> Important Factors to Consider for a Successful Localization
💡 Effective localization will help you win your customers’ hearts—and boost your business success in China!
